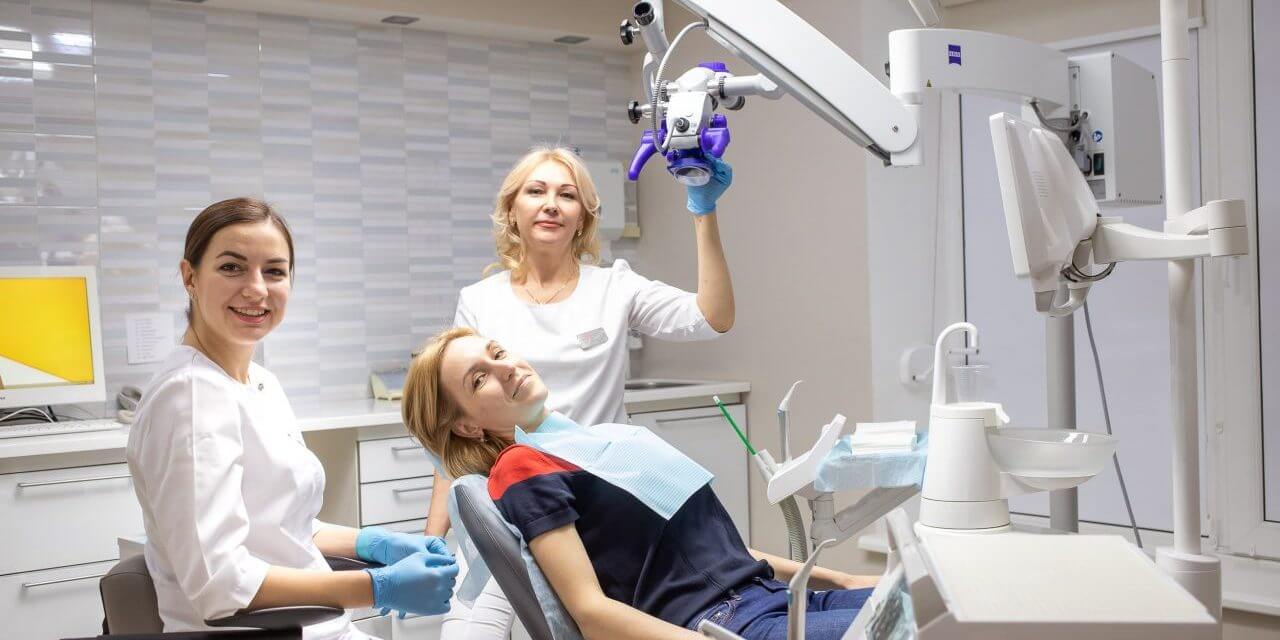
Maxillofacial surgery is a key area of expertise at Professor Vesova’s clinic. Procedures are performed by renowned surgeons—Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery at NUOZ of Ukraine named after P.L. Shupyk, Elena Petrovna Vesova, and Candidate of Medical Sciences Anna Igorevna Krivosheeva, in collaboration with top anesthesiologists.
Symptoms and Issues Requiring a Consultation at Professor Vesova’s Clinic
- Extraction of improperly positioned or impacted wisdom teeth
- Dental implant placement
- Reduced bone volume after tooth extraction
- Exposed tooth roots
- Formation of cysts in the jawbone and soft tissues
- Soft tissue neoplasms
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Jaw clicking or unusual noises in the ears while chewing
- Tooth wear
- Facial trauma from accidents
- Consequences of unsuccessful surgeries or treatments
- Short lingual or labial frenulum
Types of Surgical Procedures and Therapies Available at Prof. Vesova’s Clinic
- Tooth Extractions
- Removal of Atypical & Wisdom Teeth
- Dental Implants
- Jaw Cyst Removal
- Benign Tumor Removal (Jaw & Soft Tissues)
- Granuloma Removal
- Minimally Invasive Sinusotomy
- Bone Grafting & Volume Restoration
- Sinus Lift (Open & Closed Bone Reconstruction)
- Surgical Treatment of Periodontitis
- Frenulum Plastic Surgery (Including Z-Plasty)
- Flap Surgeries
- Salivary Gland Disease Treatment
- Open & Closed Curettage
- Post-Trauma Corrections
- Vestibuloplasty
- Gingivoplasty
- Oral Soft Tissue Plastic Surgery
- Gum Recession Treatment
- Aesthetic Dental Surgery
- Facial Contouring Surgery
- …and many more procedures based on medical indications.


0
Surgical Procedures Performed

0
Scientific Publications

0
%
Dental Implant Success Rate
0
%
Overall Surgery Success Rate
0
Years of Medical Experience
Video Testimonials
Service Pricing
Hygiene and periodontology
Service name
Price, UAH
Vestibuloplasty 1 level of complexity
7 150
Dental implantation
Service name
Price, UAH
Consultation with a maxillofacial surgeon, MD, professor
1 800
Consultation with a maxillofacial surgeon, PhD
1 200
Surgery
Service name
Price, UAH
Biopsy
1 450
Closed curettage 1 segment
7 100
Closed sinus lift
18 700
Consultation with a maxillofacial surgeon, MD, professor
1 800
Consultation with a maxillofacial surgeon, PhD
1 200
Gentle antrotomy 1st level of difficulty
19 500
Frenulectomy (plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue and lips) 1 level of complexity
5 050
Cystectomy (cyst removal) 1st level of difficulty
12 950
Gingivoplasty: surgical correction of the gingival margin 1 level of complexity
10 550
Osteoplasty with autogenous bone
6 850
Opening of subperiosteal abscess
1 850
Opening of periodontal abscess
1 650
Open sinus lift
33 800
Open curettage 1 segment
10 000
Osteotomy
3 200
Removal of a stone from the salivary gland duct
8 450
Removal of jaw neoplasms 1st level of complexity
19 550
Removal of neoplasms of soft tissues of the oral cavity, tongue, skin 1 level of complexity
9 000
Surgical intervention with removal of atypical and impacted teeth
5 800 — 16 250
Tooth extraction
1 550 — 3 850
Tooth-preserving surgery
2 750 — 4 600
Vestibuloplasty 1 level of complexity
7 150
Leave your review about us!
Your opinion is valuable to us